SCS
0.0200

A Chinese rover has found new evidence to support the theory that Mars was once home to a vast ocean, including tracing some ancient coastline where water may once have lapped, a study said Thursday.
The theory that an ocean covered as much as a third of the Red Planet billions of years ago has been a matter of debate between scientists for decades, and one outside researcher expressed some scepticism about the latest findings.
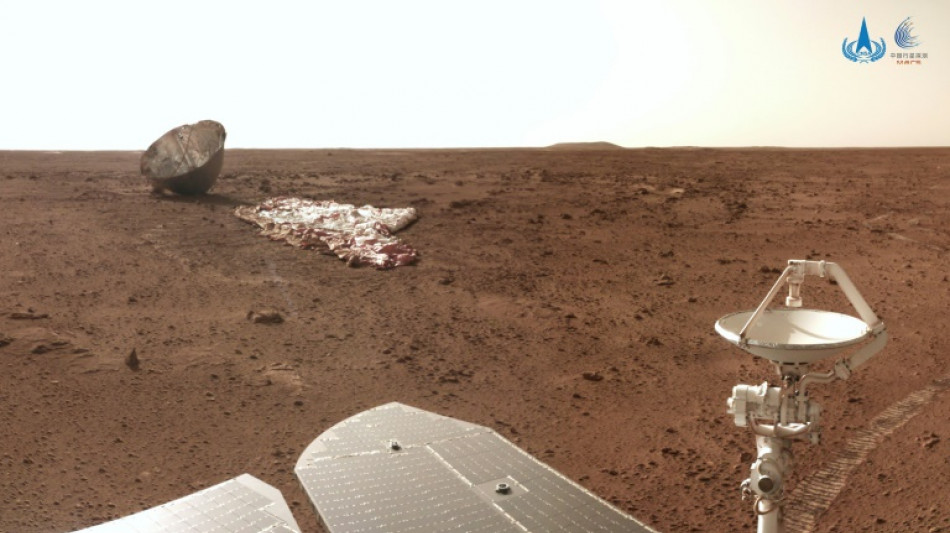
In 2021, China's Zhurong rover landed on a plain in the Martian northern hemisphere's Utopia region, where previous indications of ancient water had been spotted.
It has been probing the red surface ever since, and some new findings from the mission were revealed in the new study in the journal Nature.
Lead study author Bo Wu of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University told AFP that a variety of features suggesting a past ocean had been spotted around Zhurong's landing area, including "pitted cones, polygonal troughs and etched flows".
Previous research has suggested that the crater-like pitted cones could have come from mud volcanoes, and often formed in areas where there had been water or ice.
Information from the rover, as well as satellite data and analysis back on Earth, also suggested that a shoreline was once near the area, according to the study.
The team of researchers estimated that the ocean was created by flooding nearly 3.7 billion years ago.
Then the ocean froze, etching out a coastline, before disappearing a little 3.4 billion ago, according to their scenario.
Bo emphasised that the team does "not claim that our findings definitively prove that there was an ocean on Mars".
That level of certainty will likely require a mission to bring back some Martian rocks to Earth for a closer look.
- The coast is always changing -
Benjamin Cardenas, a scientist who has analysed other evidence of a Martian ocean, told AFP he was "sceptical" of the new study.
He felt the researchers did not take enough into account how much the strong Martian wind had blown around sediment and worn down rocks over the past few billion years.
"We tend to think of Mars of being not very active, like the Moon, but it is active!" said Cardenas of Pennsylvania State University in the United States.
He pointed to past modelling research which suggested that "even the slow Martian erosion rates" would destroy signs of a shoreline over such a long period.
Bo acknowledged that wind might have worn down some rocks, but said the impact of meteors hitting Mars can also "excavate underground rock and sediment to the surface from time to time".
While the overall theory remains contentious, Cardenas said he tended "to think there was an ocean on Mars".
Finding out the truth could help unravel a greater mystery: whether Earth is alone in the Solar System in being capable of hosting life.
"Most scientists think life on Earth sprung up either under the ocean where hot gases and minerals from the subsurface came to the seafloor, or very close to the interface of water and air, in little tidal pools," Cardenas said.
"So, evidence for an ocean makes the planet appear more hospitable."
A.El-Sewedy--DT