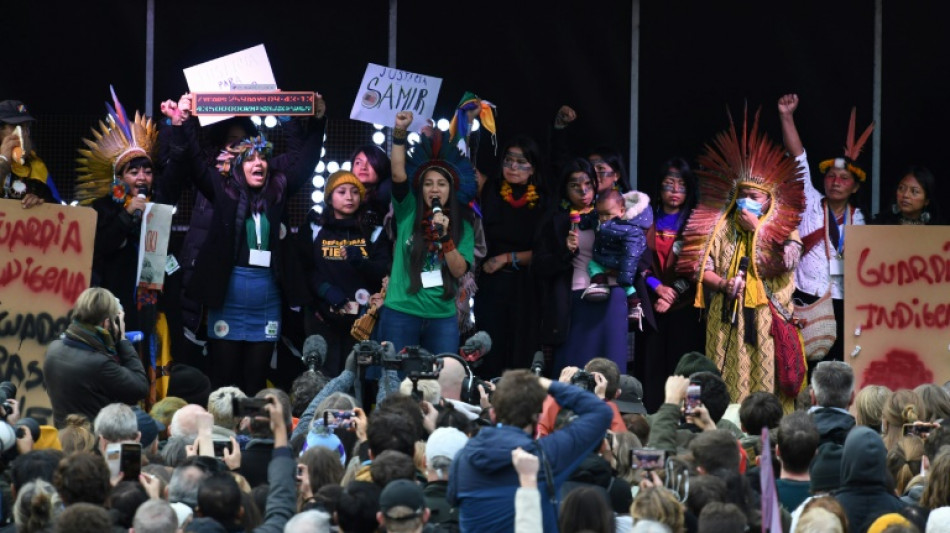
SCS
0.0200
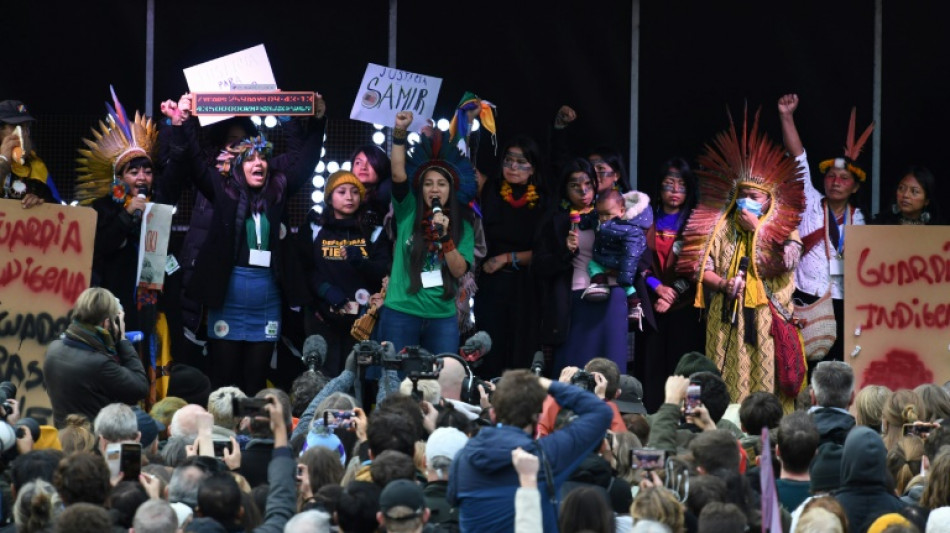
Long portrayed as victims of climate change, indigenous peoples who have struggled for years to protect ancestral lands and ways of life from destruction are finally being recognised as playing an important role in defending precious environments.
"In the face of climatic, economic and health catastrophes, reality forces the recognition of indigenous peoples' knowledge, and a new relationship of respect," said Gregorio Mirabal, head of the COICA indigenous organisation.
"Now we are not victims, we are the solution!"
That message was reinforced in a sweeping report by UN climate experts on the impacts and adaptation to global warming, released on Monday, that outlined in harrowing detail the challenges facing humanity and the planet they depend upon for survival.
It highlights that many indigenous peoples are on the frontlines of global warming, such as those in the Arctic whose communities and traditions are threatened by melting sea ice and rising waters.
But it also underscores what these communities and their intimate knowledge of nature -- transmitted from generation to generation -- can bring to the fight against climate change, in particular to limiting its impacts.
That is crucial since indigenous communities, who number less than half a billion people worldwide, steward land home to 80 percent of Earth's remaining biodiversity, notes the IPCC.
From the Amazon to Siberia, these communities have been forced to develop methods of coping with external challenges "for centuries and have developed strategies for resilience in changing environments that can enrich and strengthen other adaptation efforts", it said.
A major cause of their vulnerability acknowledged for the first time by the IPCC in this report is colonialism.
"I think it's a huge advancement," said Sherilee Harper, of the University of Alberta, Canada, adding that this is a crucial context that helps not only understand the problems facing indigenous groups, but also to frame solutions.
Harper was among the authors of the IPCC report, which also included indigenous contributors and peer reviewers for the first time.
Previously, she told AFP, "there was a tendency to paint them as victims of climate change" without the agency to act.
"Of course, that is not true."
- 'Arrogance' -
Indigenous groups have welcomed the IPCC's recognition of ancestral knowledge, but say the situation requires more than words.
"We need to come up with some kind of action-oriented strategy," said Rodion Sulyandziga, of the International Indigenous Peoples Forum on Climate Change.
"We need to combine all our efforts. We can bring to the table indigenous knowledge not just on prevention, but on new technology too."
Crucially, leveraging traditional knowledge for adapting to climate change depends on restoring rights to ancestral lands, said Sulyandziga, who represents the Indigenous Udege People of Russia -- Udege means "forest people".
"Without our land, we cannot adapt," he said.
IPCC scientists also stress the importance of "self-determination" and recognising indigenous rights.
Chapter after chapter, region after region, the thousands of pages of the report give multiple examples of adaptation practices that could serve as inspiration for the climate threats that scientists warn are already starting to have a severe impact across the world.
Take wildfires. Indigenous communities know how to fight fire with fire, burning certain plots at specific times of the year to prevent blazes from getting out of control later.
IPCC experts also mention the attention paid to the diversification of crops, like in the agroforestry system of the Kichwas of Ecuador who grow food crops and medicinal plants under the canopy of the Amazon rainforest.
Or even the use of traditional knowledge in Fiji to identify endemic plant species that can help limit coastal erosion.
Harper said everyone can benefit from learning this wisdom, once people -- especially in the West -- set aside their "arrogance".
"We have understood for thousands of years when there is balance and imbalance; it is our home and we recognise the limits," said COICA's Mirabal.
"Our bond with mother nature allows us to take care of what really matters -- water, earth, life."
But the IPCC warned that given the scale of climate change impacts, there are hard limits to adaptation.
While some communities may have to leave their homes, others have seen climate change fundamentally alter the land around them such that what was once familiar becomes strange.
Like the Inuit communities in and around the Arctic, where warming is faster than almost anywhere on Earth and the once-dependable snow and sea ice are now fragile and fleeting.
Ashlee Cunsolo, another author of the IPCC report, said colonialist regimes inflicted terrible injuries over generations -- from the erosion of language and culture to forced relocation.
People said they had "finally entered into this period of indigenous self-determination," said Cunsolo. They were "reclaiming culture" and lands.
"And then climate change comes in."
G.Rehman--DT