SCS
0.0200

The chemistry Nobel was awarded on Wednesday to three scientists who discovered a revolutionary way of making materials full of tiny holes that can do everything from sucking water out of the desert air to capturing climate-warming carbon dioxide.
The particularly roomy molecular architecture, called metal-organic frameworks, has also allowed scientists to filter "forever chemicals" from water, smuggle drugs into bodies -- and even slow the ripening of fruit.
After Japan's Susumu Kitagawa, UK-born Richard Robson and American-Jordanian Omar Yaghi won their long-anticipated Nobel Prize, here is what you need to know about their discoveries.
- What are metal-organic frameworks? -
Imagine you turn on the hot water for your morning shower, David Fairen-Jimenez, a professor who studies metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) at the University of Cambridge, told AFP.
The mirror in your bathroom fogs up as water molecules collect on its flat surface -- but it can only absorb so much.
Now imagine this mirror was made of a material that was extremely porous -- full of tiny holes -- and these holes were "the size of a water molecule," Fairen-Jimenez said.
This material would be able to hold far more water -- or other gases -- than seems possible.
At the Nobel ceremony, this secret storage ability was compared to Hermione's magical handbag in Harry Potter.
The inside space of a couple of grams of a particular MOF "holds an area as big as a football pitch," the Nobels said in a statement.
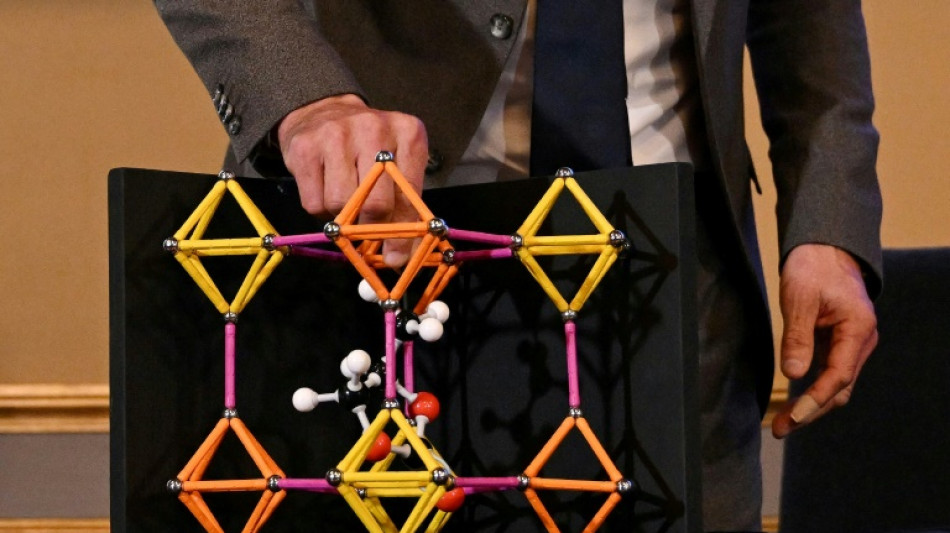
Ross Forgan, a professor of materials chemistry at the University of Glasgow, told AFP to think of MOFs as "solids that are full of holes".
They could look essentially like table salt, but "they have a ridiculously high storage capacity inside them because they are hollow -- they can soak up other molecules like a sponge."
- What did the Nobel-winners do? -
In the 1980s, Robson taught his students at Australia's University of Melbourne about molecular structures using wooden balls that played the role of atoms, connected by rods representing chemical bonds.
One day this inspired him to try to link different kinds of molecules together. By 1989, he had drawn out a crystal structure similar to a diamond's -- except that it was full of massive holes.
French researcher David Farrusseng compared the structure of MOFs to the Eiffel Tower. "By interlocking all the iron beams -- horizontal, vertical, and diagonal -- we see cavities appear," he told AFP.
However Robson's holey structures were unstable, and it took years before anyone could figure out what to do with them.
In 1997, Kitagawa finally managed to show that a MOF could absorb and release methane and other gases.
It was Yaghi who coined the term metal-organic frameworks and demonstrated to the world just how much room there was in materials made from them.
- What can they do? -
Because these frameworks can be assembled in different ways -- somewhat like playing with Lego -- companies and labs around the world have been testing out their capabilities.
"This is a field that's generating incredible enthusiasm and is moving extremely fast," Thierry Loiseau of French research centre CNRS told AFP.
More than 100,000 different kinds have already been reported in scientific literature, according to a Cambridge University database.
"Every single month, there are 500 new MOFs," Fairen-Jimenez said.
He and Forgan agreed that likely the greatest impact MOFs will have on the world are in the areas of capturing carbon and delivering drugs.
Though much hyped, efforts to capture carbon dioxide -- the driver of human-caused global warming -- have so far failed to live up to their promise.
Forgan said he was once "a bit sceptical about carbon capture, but now we're finally refining (the MOFs) to the point where they are meeting all the industrial requirements".
Canadian chemical producer BASF says it is the first company to produce hundreds of tons of MOFs a year, for carbon capture efforts.
And Yaghi himself has demonstrated that a MOF material was able to harvest water vapour from the night air in the desert US state of Arizona.
Once the rising Sun heated up the material, his team collected the drinkable water.
U.Siddiqui--DT