SCS
0.0200

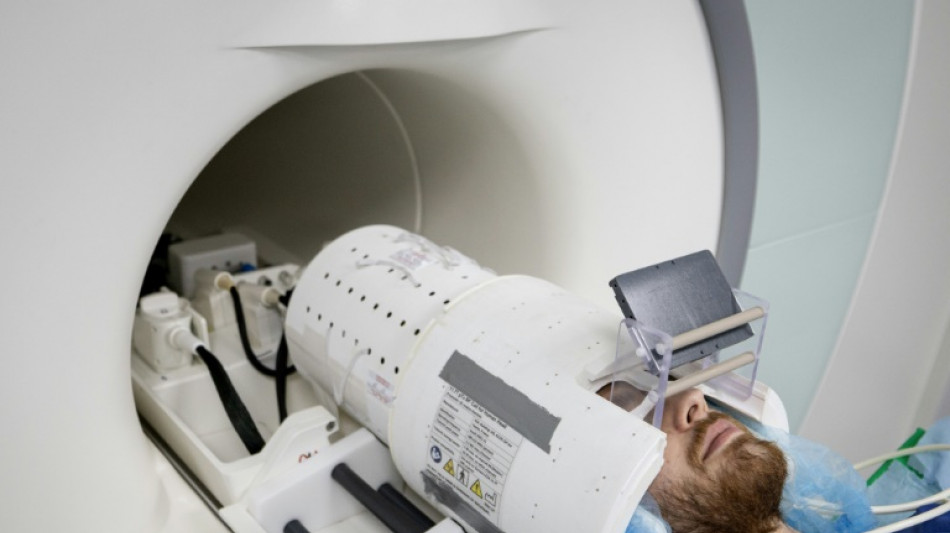
The world's most powerful MRI scanner has delivered its first images of human brains, reaching a new level of precision that is hoped will shed more light on our mysterious minds -- and the illnesses that haunt them.
Researchers at France's Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) first used the machine to scan a pumpkin back in 2021. But health authorities recently gave them the green light to scan humans.
Over the past few months, around 20 healthy volunteers have become the first to enter the maw of the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine, which is located in the Plateau de Saclay area south of Paris, home to many technology companies and universities.
"We have seen a level of precision never reached before at CEA," said Alexandre Vignaud, a physicist working on the project.
The magnetic field created by the scanner is a whopping 11.7 teslas, a unit of measurement named after inventor Nikola Tesla.
This power allows the machine to scan images with 10 times more precision than the MRIs commonly used in hospitals, whose power does not normally exceed three teslas.
On a computer screen, Vignaud compared images taken by this mighty scanner, dubbed Iseult, with those from a normal MRI.
"With this machine, we can see the tiny vessels which feed the cerebral cortex, or details of the cerebellum which were almost invisible until now," he said.
France's research minister Sylvie Retailleau, herself a physicist, said "the precision is hardly believable!"
"This world-first will allow better detection and treatment for pathologies of the brain," she said in a statement to AFP.
- Lighting up the brain's regions -
Inside a cylinder that is fives metres (16 feet) long and tall, the machine houses a 132-tonne magnet powered by a coil carrying a current of 1,500 amps.
There is a 90-centimetre (three-foot) opening for humans to slide into.
The design is the result of two decades of research by a partnership between French and German engineers.
The United States and South Korea are working on similarly powerful MRI machines, but have not yet started scanning images of humans.
One of the main goals of such a powerful scanner is to refine our understanding of the anatomy of the brain and which areas are activated when it carries out particular tasks.
Scientists have already used MRIs to show that when the brain recognises particular things -- such as faces, places or words -- distinct regions of the cerebral cortex kick into gear.
Harnessing the power of 11.7 teslas will help Iseult to "better understand the relationship between the brain's structure and cognitive functions, for example when we read a book or carry out a mental calculation," said Nicolas Boulant, the project's scientific director.
- On the trail of Alzheimer's -
The researchers hope that the scanner's power could also shed light on the elusive mechanisms behind neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's or Alzheimer's -- or psychological conditions like depression or schizophrenia.
"For example, we know that a particular area of the brain -- the hippocampus -- is implicated in Alzheimer's disease, so we hope to be able to find out how the cells work in this part of the cerebral cortex," said CEA researcher Anne-Isabelle Etienvre.
The scientists also hope to map out how certain drugs used to treat bipolar disorder, such as lithium, distribute through the brain.
The strong magnetic field created by the MRI will give a clearer image of which parts of the brain are targeted by lithium. This could help identify which patients will respond better or worse to the drug.
"If we can better understand these very harmful diseases, we should be able to diagnose them earlier -- and therefore treat them better," Etienvre said.
For the foreseeable future, regular patients will not be able to use Iseult's mighty power to see inside their own brains.
Boulant said the machine "is not intended to become a clinical diagnostic tool, but we hope the knowledge learned can then be used in hospitals".
In the coming months, a new crop of healthy patients will be recruited to get their brains scanned.
The machine will not be used on patients with conditions for several years.
A.Krishnakumar--DT