RBGPF
1.3800

The US Department of Energy's nuclear fusion laboratory says there will be a "major scientific breakthrough" announced Tuesday, as media report that scientists have finally surpassed an important milestone for the technology: getting more energy out than was put in.
The announcement has the scientific community abuzz, as nuclear fusion is considered by some to be the energy of the future, particularly as it produces no greenhouse gases, leaves little waste and has no risk of nuclear accidents.
Here is an update on how nuclear fusion works, what projects are underway and estimates on when they could be completed:
- Energy of the stars -
Fusion differs from fission, the technique currently used in nuclear power plants, by fusing two atomic nuclei instead of splitting one.
In fact, fusion is the process that powers the sun.
Two light hydrogen atoms, when they collide at very high speeds, fuse together into one heavier element, helium, releasing energy in the process.
"Controlling the power source of the stars is the greatest technological challenge humanity has ever undertaken," tweeted physicist Arthur Turrell, author of "The Star Builders."
- Two distinct methods -
Producing fusion reactions on Earth is only possible by heating matter to extremely high temperatures -- over 100 million degrees Celsius (180 million Fahrenheit).
"So we have to find ways to isolate this extremely hot matter from anything that could cool it down. This is the problem of containment," Erik Lefebvre, project leader at the French Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), told AFP.
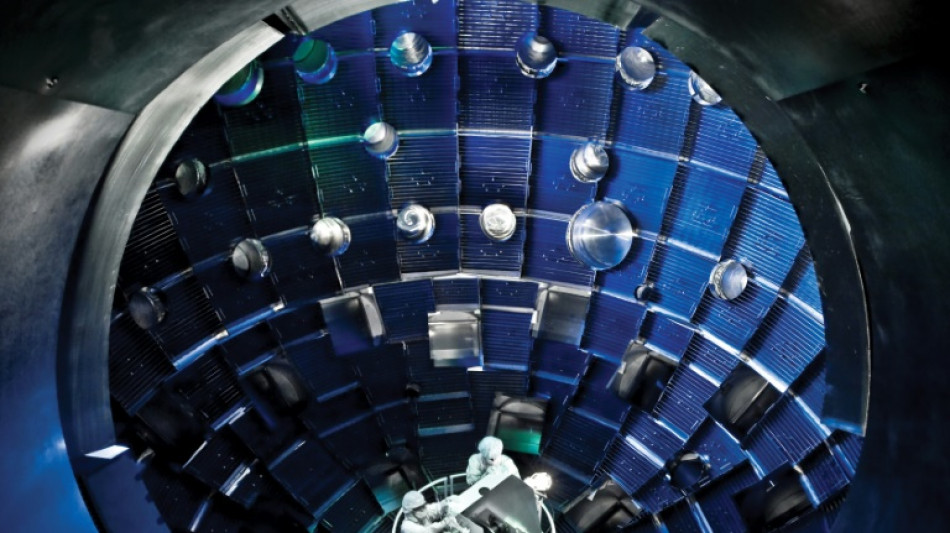
One method is to "confine" the fusion reaction with magnets.
In a huge donut-shaped reactor, light hydrogen isotopes (deuterium and tritium) are heated until they reach the state of plasma, a very low density gas.
Magnets confine the swirling plasma gas, preventing it from coming into contact with the chamber's walls, while the atoms collide and begin fusing.
This is the type of reactor used in the major international project known as ITER, currently under construction in France, as well as the Joint European Torus (JET) near Oxford, England.
A second method is inertial confinement fusion, in which high energy lasers are directed simultaneously into a thimble-sized cylinder containing the hydrogen.
This technique is used by the French Megajoule Laser (LMJ), and the world's most advanced fusion project, the California-based National Ignition Facility (NIF).
Inertial confinement is used to demonstrate the physical principles of fusion, while magnetic confinement seeks to mimic future industrial-scale reactors.
- State of research -
For decades, scientists have attempted to achieve what is known as "net energy gain" -- that is, more energy is produced by the fusion reaction than it takes to activate it.
According to reports by the Financial Times and the Washington Post, that will be the "major scientific breakthrough" announced Tuesday by the NIF.
But Lefebvre cautions that "the road is still very long" before "a demonstration on an industrial scale that is commercially viable."
He says such a project will take another 20 or 30 years to be completed.
To get there, researchers must first increase the efficiency of the lasers and reproduce the experiment more frequently.
- Fusion's benefits -
The NIF's reported success has sparked great excitement in the scientific community, which is hoping the technology could be a game-changer for global energy production.
Unlike fission, fusion carries no risk of nuclear accidents.
"If a few lasers are missing and they don't go off at the right time, or if the confinement of the plasma by the magnetic field... is not perfect," the reaction will simply stop, Lefebvre says.
Nuclear fusion also produces much less radioactive waste than current power plants, and above all, emits no greenhouse gases.
"It is an energy source that is totally carbon-free, generates very little waste, and is intrinsically extremely safe," according to Lefebvre, who says fusion could be "a future solution for the world's energy problems."
Regardless of Tuesday's announcement, however, the technology is still a far way off from producing energy on an industrial scale, and cannot therefore be relied on as an immediate solution to the climate crisis.
I.Menon--DT