SCS
0.0200

Scientists investigating how Antarctica's ice sheets retreated in the deep past have turned to an innovative approach: studying the genes of octopuses that live in its chilly waters.
A new analysis published Thursday in Science finds that geographically-isolated populations of the eight-limbed sea creatures mated freely around 125,000 years ago, signaling an ice-free corridor during a period when global temperatures were similar to today.
The findings suggest the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is closer to collapse than previously thought, threatening 3.3-5 meters of long term sea level rise if the world is unable to hold human-caused warming to the 1.5 degrees Celsius target of the Paris Agreement, said the authors.
Lead author Sally Lau of James Cook University in Australia told AFP that as an evolutionary biologist focused on marine invertebrates, "I understand and then apply DNA and biology as a proxy of changes to Antarctica in the past."
Turquet's octopus made an ideal candidate for studying WAIS, she said, because the species is found all around the continent and fundamental information about it has already been answered by science, such as its 12-year-lifespan, and the fact it emerged some four million years ago.
About half-a-foot (15 centimeters) long excluding the arms and weighing around 1.3 pounds (600 grams), they lay relatively few, but large eggs on the bottom of the seafloor. This means parents must put significant effort into ensuring their offspring hatch -- a lifestyle that prevents them traveling too far away.
They are also limited by circular sea currents, or gyres, in some of their modern habitats.
- 'Tipping point close' -
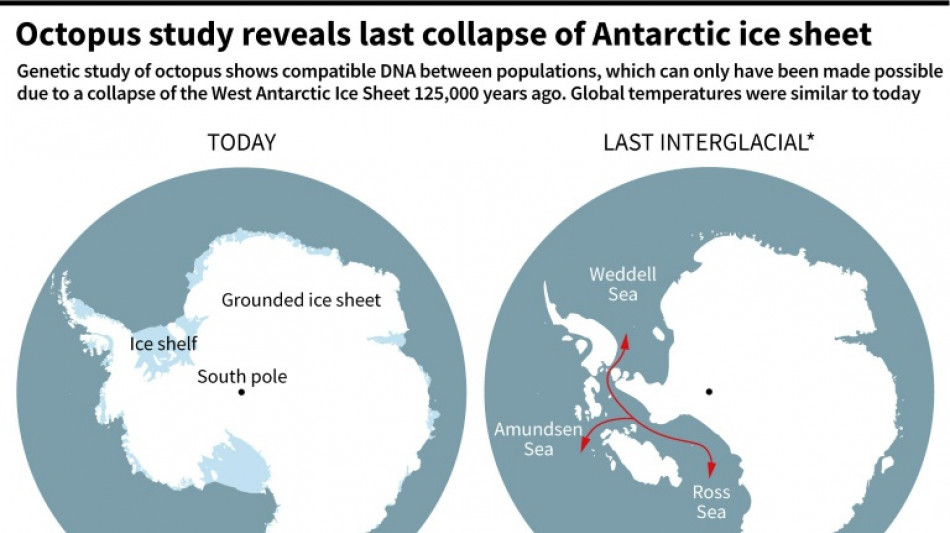
By sequencing the DNA across genomes of 96 samples that were generally collected inadvertently as fishing bycatch and then left in museum storage over the course of 33 years, Lau and colleagues found evidence of trans-West Antarctic seaways that once connected the Weddell, Amundsen and Ross seas.
The history of genetic mixing indicated WAIS collapsed at two separate points -- first in the mid-Pliocene, 3-3.5 million years ago, which scientists were already confident about, and the last time in a period called the Last Interglacial, a warm spell from 129,000 to 116,000 years ago.
"This was the last time the planet was around 1.5 degrees warmer than pre-industrial levels," said Lau. Human activity, primarily burning fossil fuels, has so far raised global temperatures by 1.2C compared to the late 1700s.
There were a handful of studies prior to the new Science paper that also suggested WAIS collapsed some time in the past, but they were far from conclusive because of the comparatively lower resolution genetic and geological data.
"This study provides empirical evidence indicating that the WAIS collapsed when the global mean temperature was similar to that of today, suggesting that the tipping point of future WAIS collapse is close," the authors wrote.
Sea level rise of 3.3 meters would drastically alter the world map as we know it, submerging low-lying coastal areas everywhere.
Writing in an accompanying commentary piece, Andrea Dutton of the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Robert DeConto of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst described the new research as "pioneering," adding it posed intriguing questions about whether ancient history will be repeated.
They flagged however that several key questions remained unanswered -- such as whether the past ice sheet collapse was caused by rising temperatures alone, or whether other variables like changing ocean currents and complex interactions between ice and solid Earth were also at play.
It's also not clear whether the sea level rise would be drawn out over millennia or occur in more rapid jumps.
But uncertainties such as these can't be an excuse for inaction against climate change "and this latest piece of evidence from octopus DNA stacks one more card on an already unstable house of cards," they wrote.
Y.Amjad--DT