SCS
0.0200

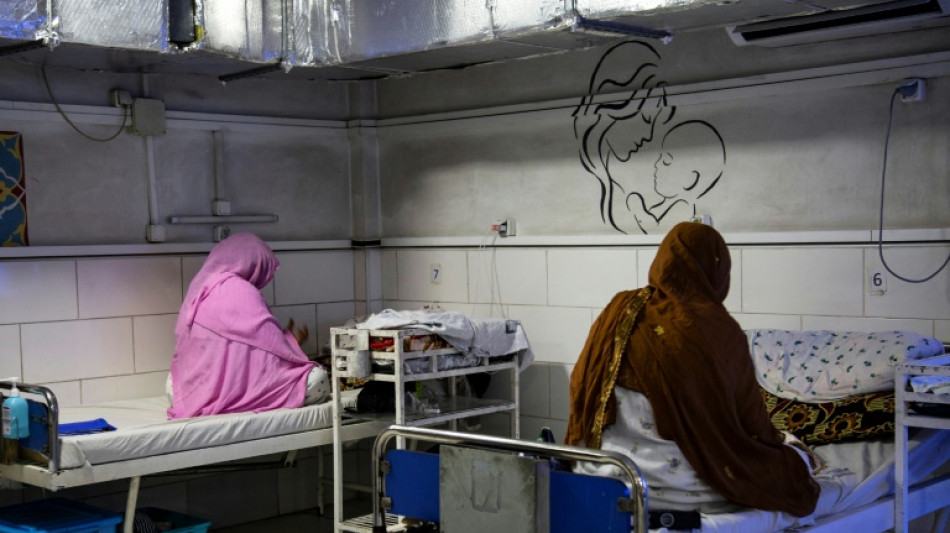
Zubaida travelled from the rural outskirts of Khost in eastern Afghanistan to give birth at a maternity hospital specialising in complicated cases, fearing a fate all too common among pregnant Afghan women -- her death or her child's.
She lay dazed, surrounded by the unfamiliar bustle of the Doctors Without Borders (MSF)-run hospital, exhausted from delivery the day before, but relieved.
Her still-weak newborn slept nearby in an iron crib with peeling paint, the child's eyes lined with khol to ward off evil.
"If I had given birth at home, there could have been complications for the baby and for me," said the woman, who doesn't know her age.
Not all of the women who make it to the hospital are so lucky.
"Sometimes we receive patients who come too late to save their lives" after delivering at home, said Therese Tuyisabingere, the head of midwifery at MSF in Khost, capital of Khost province.
The facility delivers 20,000 babies a year, nearly half those born in the province, and it only takes on high-risk and complicated pregnancies, many involving mothers who haven't had any check-ups.
"This is a big challenge for us to save lives," said Tuyisabingere.
She and the some 100 midwives at the clinic are on the front lines of a battle to reduce the maternal mortality rate in Afghanistan, where having many children is a source of pride, but where every birth carries heavy risks -- with odds against women mounting.
Afghanistan is among the worst countries in the world for deaths in childbirth, "with one woman dying every two hours", UN spokesman Stephane Dujarric said earlier this month.
The Afghan health ministry did not respond to repeated requests for comment on this story.
According to the latest World Health Organization figures, from 2017, 638 women die in Afghanistan for every 100,000 viable births, compared with 19 in the United States.
That figure, moreover, conceals the huge disparities between rural and urban areas.
Terje Watterdal, country director for the non-profit Norwegian Afghanistan Committee (NAC), said they saw 5,000 maternal deaths per 100,000 births in remote parts of Afghanistan.
"Men carry the women over their shoulders, and the women die over the mountain trying to reach a hospital," he said.
- 'Brain drain' -
Before the return to power of the Taliban in August 2021 and the end of their insurgency, women would sometimes have to brave the frontlines to reach help, but now there are new challenges -- including a "brain drain" of expertise.
"A lot of gynaecologists have left the country," Watterdal said.
Moreover, Taliban authorities want to get rid of the mobile medical teams visiting women because "they cannot control the health messages they were giving", he said.
Under the Taliban government, women have been squeezed from public life and had access to education restricted, threatening the future of the female medical field in a country where many families avoid sending women to male doctors.
"Access to antenatal and postnatal care for a woman was (always) extremely complicated. It's even more complicated today," said Filipe Ribeiro, MSF director in Afghanistan.
This is due to measures taken by authorities as well as the failings of the healthcare system -- including structural support from foreign donors.
"What little there was has been put under even greater pressure," Ribeiro said.
The financial strain on families amid the country's economic crisis increases the risks, said Noor Khanum Ahmadzai, health coordinator for non-governmental organisation Terre des Hommes in Kabul.
In a public hospital where the midwives are overworked and poorly paid, women have to bring their own medicine.
A delivery costs around 2,000 Afghanis ($29) -- a significant sum for many families.
Despite the risks, "women who used to go to the public sector now prefer to deliver at home, because they don't have money", said Ahmadzai.
An estimated 40 percent of Afghan women give birth at home, but that shoots up to 80 percent in remote areas -- often with the help of their mother-in-law or a local matriarch, but sometimes alone.
- 'Mother died in childbirth' -
Islam Bibi, pregnant with triplets, went to the MSF facility in Khost in pain, and empty-handed.
"I was sick, my husband didn't have any money. I was told, 'Go to this hospital, they do everything for free'," said the 38-year-old, one of hundreds of thousands of Afghans who fled Pakistan in recent months, fearing deportation.
Multiple births like Islam Bibi's are common, said Tania Allekotte, an MSF gynaecologist from Argentina.
"It is valued here to have many children and many women take a treatment to stimulate their fecundity. We often have twins here," she told AFP.
The average woman has six children in Afghanistan, but multiple pregnancies, repeated caesarean sections or miscarriages increase the risk of death.
There are some rays of hope.
Women in neighbouring Paktia province may have fewer risks now, thanks to a first-of-its-kind maternity centre opened recently by NAC in the small provincial capital Gardez -- a clinic run by women for women.
"This type of clinic doesn't exist in the majority of provinces," Khair Mohammad Mansoor, the Taliban-appointed provincial health director, told the all-male audience.
"We have created a system for them in which sharia law and all medical principles will be observed."
The NAC facility aims to help "many of our sisters who live in isolated areas", manager Nasrin Oryakhil said, with similar clinics planned for four other provinces in the coming months.
Its walls freshly painted and decorated with posters promoting vitamins and iron for pregnant women, the small clinic is set up for 10 deliveries a day, said head midwife Momina Kohistani.
Keeping mothers alive as they bring new life into the world is close to home for her.
"My mother died in childbirth," she murmured, tears rolling down her cheeks.
S.Al-Balushi--DT